 04 Apr 2024
04 Apr 2024“By following MVC principles, developers can build robust, flexible, and maintainable web applications that efficiently meet the evolving needs of users and businesses.”
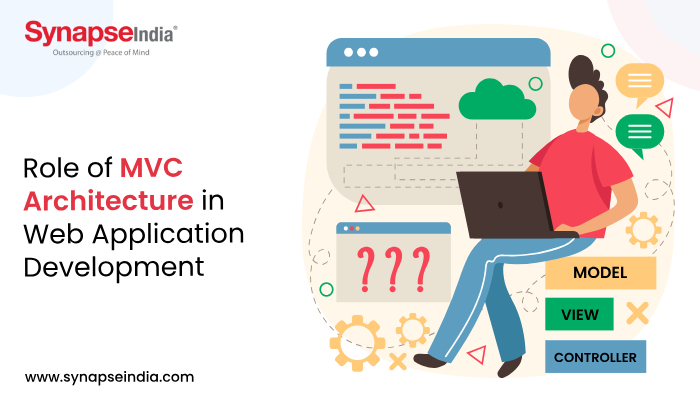
To create scalable mobile applications, the web development community is constantly looking for effective and scalable frameworks and techniques. Of them, the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture is particularly notable since it is a tried-and-true design pattern that has transformed the creation, development, and upkeep of web applications. With its structured architecture, code can be organized more effectively, concerns can be divided, and scalability, maintainability, and reusability are all increased. It separates an application into three interdependent parts, the Controller, the View, and the Model, each with specific duties and functions. MVC architecture is a key component of contemporary web development techniques, offering benefits including increased productivity and collaboration among developers as well as better code organization and modularity.
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture is a design pattern that has become synonymous with modern web development practices. It provides a structured approach to organizing code, separating concerns, and improving the maintainability and scalability of web applications. Let's dive into the key components of MVC and how they contribute to developing scalable web patterns.
A synonymous design pattern that has come to be associated with contemporary web development techniques is the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. It offers an orderly method for dividing the code, keeping web apps more manageable and scalable, and separating concerns. Now let's explore the essential elements of MVC and how they help create strong web patterns.

The Model represents the data and business logic of the application. It encapsulates the application's data structure, handles data manipulation and validation, and interacts with the database or external data sources. The Model ensures data integrity and facilitates code reusability by isolating data-related operations from the user interface.
The View is responsible for presenting the data to the user and handling user interactions. It defines the user interface components, such as HTML templates, CSS stylesheets, and client-side scripts, that render data from the Model to the user. The View remains agnostic of the underlying data and business logic, enabling developers to create flexible and customizable user interfaces.
The Controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View, handling user requests, processing data, and updating the View accordingly. It interprets user input, invokes appropriate actions on the Model, and selects the appropriate View to display the results. By decoupling user interactions from data manipulation, the Controller promotes code modularity and facilitates application flow control.
MVC architecture enables the creation of reusable and composable components that can be combined to build sophisticated web applications. Developers can leverage MVC principles to design modular and extensible patterns, such as Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) and Model-View-Presenter (MVP), which further enhance code organization and separation of concerns.

The advantages of MVP (Model-View-Presenter) architecture in web application development are numerous and can significantly impact the success of a project. Here are some key advantages:
MVP architecture promotes modularity by separating the presentation logic (View) from the business logic (Model) and user input handling (Presenter).
MVP architecture facilitates unit testing of individual components, such as Presenters and Models, in isolation from the user interface (View).
MVP architecture enables developers to modify and extend the functionality of web applications more easily. It reduces the risk of unintended side effects and simplifies maintenance and updates.
MVP architecture promotes a clear separation of responsibilities, making it easier for developers to understand and navigate the codebase.
MVP architecture allows for a more responsive and interactive user experience by decoupling user input handling (Presenter) from the user interface (View).
MVP architecture enables parallel development of different components of the web application by different teams or developers.
MVP architecture offers numerous advantages for web application development, including modularity, testability, flexibility, clarity, improved user experience, support for parallel development, and adaptability to changing requirements.
MVC architecture and its pattern for web patterns help developers streamline the development process, improve code maintainability, and enhance the user experience of web applications. Whether building simple websites or complex web applications, MVC provides a solid foundation for creating scalable and maintainable web patterns that meet the demands of modern web development. With the exploration of the role of MVC architecture in web application development, it is clear that MVC remains a vital tool in the developer's arsenal, empowering them to create innovative and user-centric applications that drive business growth and success. By embracing MVC principles and best practices, developers can build upon a solid foundation and deliver exceptional web experiences that delight users and exceed expectations.

 27 Jan 2024
27 Jan 2024
